Read About Our Work and Products in the Literature
Sivan A. Raviv, ... Assaf Zinger
Technion – Israel Institute of Technology
Researchers developed a biomimetic nanoparticle platform that overcomes a critical limitation of cell membrane derived drug delivery systems by selectively enriching specific functional proteins, leukocyte adhesion molecules (CD18, CD11a, CD11b), to enable precise targeting of inflamed endothelium. Using a 2D microfluidic blood vessel model, the protein enriched nanoparticles demonstrated significantly improved endothelial interactions and accumulation under physiological flow compared to conventional cell membrane coated particles, combining biological functionality with reproducibility and manufacturing control for translational inflammatory and targeted therapy applications.
Wenhan Wang, Kangfu Chen, Zongjie Wang
Northwestern University
This study shows that blocking the kinase PIK3CA can substantially improve how well lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) deliver siRNA. Using a genome‑wide CRISPR screen, the authors identify PIK3CA as a key, druggable regulator of LNP uptake, then demonstrate that co‑treating cells and mice with the clinical inhibitor BAY1082439 boosts LNP internalization by up to fivefold, enhances siRNA‑mediated gene silencing, and improves outcomes in both tumor and inflammatory disease models. Overall, PIK3CA inhibition emerges as a straightforward strategy to increase the efficacy of LNP‑based siRNA therapies.
Deepak K. Sahel, ... Conroy Sun, Gaurav Sahay
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, Robertson Life Sciences Building, Oregon State University
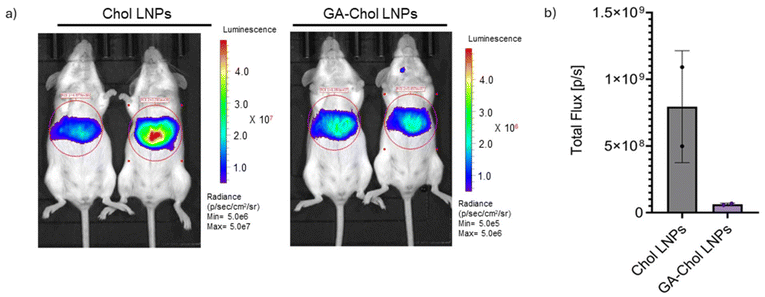
This study develops a new cholesterol derivative, glutamate–cholesterol (GA–Chol), to keep mRNA LNP transfection localized after intramuscular or intratumoral injection rather than “leaking” to the liver. Incorporating GA–Chol into LNPs increases in vitro transfection by up to ~20‑fold and, in mice, drives strong expression at the injection site with minimal hepatic transfection, enabling effective intratumoral delivery of caspase‑3 mRNA that significantly reduces and stabilizes tumor burden.
Alexander A. Cohen, Jennifer R. Keeffe ... Pamela J. Bjorkman
Division of Biology and Biological Engineering, California Institute of Technology
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is used here as a single-shot vaccine platform that delivers multiple timed “pulses” of a mosaic nanoparticle displaying RBDs from eight different SARS-like coronaviruses. In mice, ALD delivery of the mosaic-8b RBD nanoparticle generated broader and stronger cross-neutralizing antibody responses against mismatched sarbecoviruses than conventional prime–boost vaccination. The data suggest ALD could be a useful way to deploy mosaic RBD-nanoparticle vaccines to prepare for future sarbecovirus spillovers and other rapidly evolving pathogens.
Reshma Koolaparambil Mukesh, ... Neeltje van Doremalen
Laboratory of Virology, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National Institutes of Health
This study shows that adding an intranasal ChAdOx1 nCoV‑19 “mucosal” boost after an intramuscular mRNA COVID‑19 vaccine generates much stronger local immunity in the airways than intramuscular vaccination alone. Mice receiving the intranasal dose developed robust spike‑specific IgA and tissue‑resident T cells in the upper respiratory tract and remained protected there even 12 weeks later, whereas protection from intramuscular vaccination alone had waned. The results suggest mucosal vaccination could provide more durable, site‑specific protection against SARS‑CoV‑2 and potentially reduce the need for frequent systemic boosters.
Colin Basham, ... Alexander V. Kabanov, Jacob D. Ramsey
Center for Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery and Division of Pharmacoengineering and Molecular Pharmaceutics, Eshelman School of Pharmacy, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
This study develops new poly(2-oxazoline) (POx) “stealth” lipids to replace PEG in lipid nanoparticles, aiming to avoid anti-PEG antibody issues like anaphylaxis and rapid clearance. The authors show that LNPs made with short, hydrophilic POx chains significantly improve mRNA transfection in vitro and in vivo, increase expression in muscle, and shift biodistribution toward lymph nodes and spleen. These results suggest POx-lipids are a strong PEG alternative for safer, more targeted LNP vaccines and therapeutics.
Jian Hang Lam, ... Madhavan Nallani
ACM Biolabs Pte Ltd
This work describes thermostable block-copolymer nanoparticles (BNPs) that can carry mRNA and remain stable for over a year at 4 °C without loss of mRNA or carrier integrity. Compared with standard LNPs, mRNA-BNPs target lymphoid organs more effectively, generate durable antibody and CD8⁺ T cell responses after long-term refrigerated storage, and do not boost anti-PEG antibodies upon repeat dosing. In SARS-CoV-2 challenge studies, spike mRNA-BNPs protect hamsters from disease and reduce lung viral loads to a level comparable to a Comirnaty-like mRNA vaccine.
Aishwarya Vasudevan, Antony Jozić, ... Gaurav Sahay
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, Robertson Life Sciences Building, Oregon State University
This study shows that intracameral injection of lipid nanoparticles can efficiently deliver mRNA and CRISPR/Cas9 to the anterior chamber of the eye, especially the trabecular meshwork, without observable ocular toxicity. In mice, these LNPs produced strong but transient expression of reporter proteins and achieved up to about 14% gene-editing efficiency, highlighting their potential for targeted gene therapy and editing for diseases like glaucoma.
Alexander A. Cohen, Jennifer R. Keeffe ... Pamela J. Bjorkman
Division of Biology and Biological Engineering, California Institute of Technology
Immunization with mosaic-8b nanoparticles, which present eight SARS-like betacoronavirus (sarbecovirus) RBDs, elicits broader cross-reactive antibodies compared to SARS-CoV-2 RBD-only nanoparticles and offers protection against diverse sarbecoviruses. This study examined how prior COVID-19 vaccinations influence the immune response to mosaic-8b, finding that it induces more de novo antibodies targeting variant RBDs, supporting its potential to protect vaccinated or infected individuals from future SARS-CoV-2 variants and zoonotic sarbecoviruses.
Sai Nikhil Subraveti, Brian K. Wilson, Navid Bizmark, Jason Liu, Robert K. Prud'homme
Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Princeton University
A detailed protocol for synthesizing lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) using confined impinging jet (CIJ) mixer technologies, including a two-jet CIJ and a four-jet multi-inlet vortex mixer (µMIVM), is demonstrated. The CIJ mixers generate reproducible, turbulent micro-mixing environments, resulting in the production of monodisperse LNPs.
Department of Chemistry, Louisiana State University
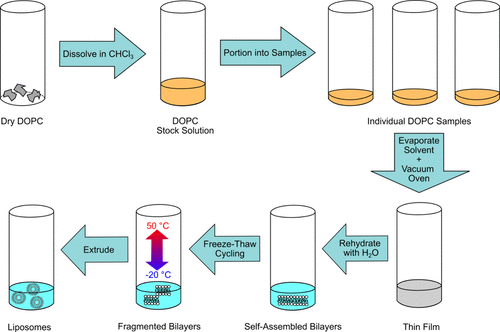
This work presents an automated extruder designed to enhance undergraduate research by providing a user-friendly system for preparing vesicles, such as liposomes, with precise size and polydispersity control. The project breaks down the development into software, hardware, and testing components, offering students hands-on experience with an accessible, simplified version of an industrial process, with all resources freely available online for further exploration and contribution.
Institute for Medical Engineering and Science, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
This study used computational methods to design nanoparticles displaying SARS-like betacoronavirus (sarbecovirus) receptor-binding domains (RBDs) with various mutations to enhance cross-reactive antibody responses. Among the designed antigens, mosaic-7COM elicited higher binding and neutralization titers in mice compared to other constructs, showing promise for protecting against highly mutated SARS-CoV-2 variants and zoonotic sarbecoviruses.


.jpg)